News & Updates
Cup-lump Shortage Hits Liberia’s TSR Industry
Experts seek policy intervention to ban cup-lump exports
Block rubber or TSR processing factories in Liberia are increasingly challenged by a widening shortage of cup-lump in the country. With the recent opening of greenfield factories and capacity addition in the factories that existed from before, the country has the total capacity to produce 165,000 tons of TSR annually. To cater its TSR factories, the country annually needs around 254,000 tons of cup-lump (Measured in wet weight). However, the current level of domestic production of cup-lump is only around 185,000 tons (120,000 tons in dry weight) which represents only 65% of the quantity needed to run the factories. It means, operational efficiency and economic sustainability of the TSR factories in Liberia are increasingly challenged by an acute shortage of cup-lump. The following table helps to understand the gravity of the cup-lump shortage in the country.
| No. of shifts | Capacity of TSR Production (Tons/hour) | Annual Capacity, in tons (25 days/11 months) | Annual requirement of cup-lump (Wet weight in tons based on 65% dry rubber content) | |
| LAC | 3 | 5 | 33,000 | 50,770 |
| Firestone | 3 | 13 | 85,000 | 132,000 |
| Jeety Rubber | 3 | 5 | 33,000 | 50,770 |
| Lee | 2 | 3 | 13,200 | 20,300 |
| Nimba | 0 | 0 | – | – |
| All together | 26 | 165,000 | 253,840 |
Despite TSR factories facing such a huge shortage of raw material, a considerable portion of the domestic production of cup-lump goes out of the country by way of exports. To help the TSR processing factories have domestic availability of raw material, Liberia should immediately impose a total ban of exports. Such a policy intervention assumes significance from a wider developmental perspective on account of the following points:
- TSR processing factories in Liberia are compelled to scale down capacity utilization due to the domestic shortage of raw material. The lower capacity utilization impacts on the operational efficiency, unit cost of production, and global competitiveness of Liberian TSR. Persistent under-utilization of capacity poses a serious threat to the economic sustainability of TSR industry in the country.
- TSR processing factories in Liberia play a crucial role in the country’s rural employment generation, rural income and rural economic development. As an effective tool to strengthen rural economy and uplift the economic well-being of the rural community, government should consider strengthening the TSR processing factories by addressing the shortage of raw material.
- For the economic development of a country, value addition of raw materials should take place within the country. When value addition takes place within the country, it contributes to the economy by way of employment generation, development of ancillary sectors, and higher rural income. The higher rural income triggers rural demand for goods and services, and thereby contributes to the national economy. Higher rural income also contributes to the socio-economic uplift of economically weaker sections. Moreover, exports of value-added products bring much higher foreign exchange than raw materials.
It merits mention that Ivory Coast has imposed a ban on the exports of cup-lump from the country effective from 1 Jan 2024 as a measure to encourage domestic value addition. Due to the ban imposed by Ivory Coast, it is no longer possible for Liberia to bridge the shortage of cup-lump by importing from there. The recent capacity addition in TSR processing in Ghana and other West African countries signals that Liberia will not be able rely on these countries for sourcing cup-lump.
The above points justify the case for the Government of Liberia to ban the export of cup-lump and other unprocessed forms of natural rubber from the country with immediate effect.
#Liberia #BlockRubber #CupLump #RubberPolicy #WhatNextRubber #RuralDevelopment #RuralEconomy #MillenniumDevelopmentGoal #Commodity #ValueAddition #naturalRubber
India’s Sheet Rubber Market Misses the Global Rally. Is this a New Normal?
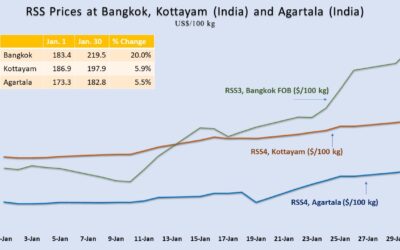
The prices of RSS3 at Bangkok FOB, the global benchmark grade of ribbed smoked sheet of natural rubber, soared 20% over the first 30 days of January 2024. RSS prices at Bangkok are poised to scale further up and continue along a rising curve for the next six months, as per the emerging supply-demand outlook from WhatNext Rubber Media.
Kottayam Market Stays almost Immune to Global Rally
In India, around 70% of the total production of natural rubber (NR) is processed and traded in the form of RSS. This is in sharp contrast with the global pattern where TSR or “block rubber” contributes around 65% of the output. “RSS4 at Kottayam” is India’s benchmark reference price for NR (Kottayam is the largest NR producing district in the State of Kerala, the traditional rubber-growing region of India). Surprisingly, RSS4 prices at Kottayam rose only 6% during the first 30 days in Jan 2024 against a 20% jump at Bangkok market during the same period. Kottayam market used to rule above the Bangkok market by 20% to 30%. Moreover, Kottayam market used to track the rally at Bangkok market. In sharp contrast with the earlier pattern, Kottayam market stayed almost immune to the sharp gains at Bangkok market in January. Moreover, Bangkok market crossed over Kottayam market on January 12, 2024. (Please see the chart given above). What are the factors that prevented Kottayam market from gaining in tandem with the 20% surge at Bangkok market? Is this a temporary phenomenon, or a new normal?
Indian Auto-Tyre Industry Shifts from RSS to TSR
A comparison between the RSS markets in India and Thailand used to be relevant during the past when Indian auto tyre manufacturing companies predominantly consumed RSS unlike the TSR-dominant manufacturing followed by their counterparts outside the country. Over the past nearly 10 years, the Indian auto tyre companies have largely shifted to a TSR-based manufacturing by deviating from the hitherto followed RSS-based manufacturing. Because of the RSS-based manufacturing followed in the past, auto-tyre companies in the country used to source NR after making a comparison between the cost of domestic RSS and imported RSS. That practice has changed over the past 10 years due to the shift from RSS to TSR. The Indian auto tyre manufacturing industry currently turns to domestic RSS only is it is economically more attractive than souring TSR from overseas. It means, the cost of imported RSS is no more relevant to the Indian auto-tyre companies due to the shift to TSR. The prices of TSR are considerably below RSS prices. The point is that the shift from RSS to TSR by the Indian auto-tyre manufacturing companies has made Kottayam RSS market almost insensitive to the RSS market at Bangkok.
Sourcing Shifts from Indonesia to Ivory Coast
Auto-tyre manufacturing companies in India have recently shifted their sourcing of TSR. Earlier they used to source TSR largely from Indonesia and other southeast Asian NR producing countries. Ivory Coast has become the preferred source for the Indian auto tyre companies for sourcing TSR over the past two years. It means that auto-tyre manufacturing companies in India currently source RSS from domestic market only if they find it more economic than souring TSR from Ivory Coast. From this perspective, it is the TSR prices prevailing in Ivory Coast that influences the Kottayam RSS market rather than the RSS prices at Bangkok. The close link between the Indian RSS market and the Bangkok RSS market is a story of the past which is no more relevant in the changed scenario.
Increasing Influence of Low-Cost Rubber from Northeast India
In meeting the demand for RSS, Indian tyre industry can now increasingly rely on northeast India which is a non-traditional region having considerable cost advantage over the traditional region (State of Kerala). In the northeast India, the prices of RSS4 (Agartala Market is the reference market for northeast India) are around 10% lower compared to Kottayam. India’s northeast currently accounts for around 20% of the country’s total output of NR. As a new trend, major auto tyre manufacturing companies currently bring RSS from northeast India to their factories located in Kerala because of the substantial cost advantage. It means, the RSS market in Kerala currently faces competition not from imported RSS, but from the RSS produced within India, in the country’s northeast, at a substantially lower cost. The low-cost RSS coming from northeast India is exerting a downward pressure on RSS market in the traditional region, especially the State of Kerala. This trend in expected to continue with an increasing influence. It means, it’s not a temporary happening, but a new normal.
Northeast India to Contribute more than 50% of India’s Rubber Output
The Rubber Board, by joining hands with India’s Auto Tyre Manufacturers’ Association (ATMA), has launched a massive rubber cultivation project in northeast India envisaging expansion of rubber cultivation by 200,000 hectares by 2025. This can bring an additional output of around 300,000 tons per year when the planted trees attain maturity by early 2030s. With this additional production, the share of northeast India in the country’s total production is expected to go beyond 50%, from the current level of 20% (Northeast India is projected to produce around 525,000 tons of NR by 2032 if the ongoing planting programme in the region achieves the target). It means, the Kottayam RSS market should expect more dominating negative influence of the low-cost RSS coming from northeast India in the years ahead.
Kerala’s Shrinking Rubber Map
With the increasing dominance of low-cost NR from northeast India, rubber farmers in the State of Kerala will be ultimately left with no option but selling the produce at prices matching with those prevailing at Agartala. The dominating influence of low-cost NR from northeast India, along with the abnormally high wages in Kerala, higher cost of material inputs, and a considerably lower purchasing power of rupee in the state, will make rubber cultivation economically unviable in Kerala. It means, parallel to the expansion of cultivation in the northeast India, Kerala should expect a marked shrinkage of rubber area. The possibility of Kerala getting almost fully wiped out from India’s natural rubber production map cannot be ruled out.
Prices are Right for Exports
Conditions are now ideal for India to exploit the higher RSS prices overseas. The wide gap between the RSS prices at Kottayam and Bangkok, and that between Agartala and Bangkok, offer immense scope for India to tap the global rally in RSS prices and thereby support the farmers. A policy initiative along this direction can also help Indian RSS market to gain momentum and move in tandem with the surging Bangkok market.
Are Natural Rubber Prices Gearing up for a Trend-break?
Natural rubber (NR) market foresees a potential tight supply emerging globally by the end of the first quarter of 2024. The trends up to October point to a massive fall in production in major producing countries for the full year 2023.
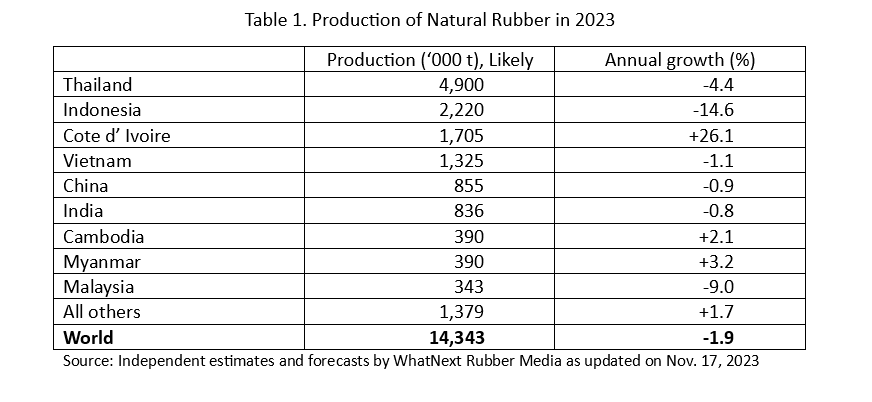
The production in Thailand, the world’s largest producer and exporter, fell by an annualized 9.0% in the third quarter (Jul-Sep 2023). The full-year production in Thailand is heading to a 4.4% fall. Coming to the second largest producer Indonesia, the production in 2023 is expecting a massive 14.6% fall. Malaysia is expecting a 9.0% fall in its NR output during 2023. Coming to other major producing countries, the production is expected to marginally fall in Vietnam (-1.1%), China (-0.9%) and India (-0.8%). However, a whopping 26.1% increase expected in the production from Cote d’Ivoire can partly offset the lower production in the above countries.
Total world production during 2023 is expected at 14.343 million tons, down 1.9% from the year before. Please see Table 1 for getting a consolidated picture.
World Supply Wiped Out by 0.7 Million Tons
As per the outlook reported by WhatNext Rubber Media International in mid-2023, the six-month period from July to Dec 2023 was projected to generate a total surplus of 1.4 million tons, and this would have been adequate to bridge the total deficit of 1.4 million tons projected for the subsequent six months (i.e., from Jan to Jun 2024). However, the scenario has now been drastically changed largely due to the sharp fall in production in Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia. The unexpected major output fall in these three countries along with the marginal fall in Vietnam, China, and India have wiped out around 0.7 million tons from the world output expected for 2023. It means the carryover stock available for meeting the shortage expected for the first half of 2024 is now lower by 0.7 million tons from the quantity projected in mid-2023.
Carryover from Pre-2023 Period
To bridge the shortage expected for the first half of 2024, another possibility is to use the stock accumulated over several years prior to 2023. But the world supply was deficit both in 2021 and 2022. Moreover, the larger part of the prior years’ accumulated stock should have been absorbed to meet the deficit in the first half of 2023. The supply during the first half of 2023 was short of the demand by 1.5 million tons. It means an estimated quantity of 1.5 million tons was already used from the stock accumulated prior to 2023. It implies the market cannot count much on the prior years’ accumulated stock. Such a situation points to a tight supply condition potentially emerging by around March 2024. The tight supply condition anticipated by March 2024 can potentially intensify in the succeeding five months (i.e., from Apr to Aug 2024) and possibly evolve into a global shortage in between.
Potential Rebound in Demand by Q4 2024
Economic activities in the U.S. and Europe are expected to start improving by the second half of 2024 triggered by the monetary policy easing by the respective central banks. The most recent inflation trends and key economic readings indicate the possibility of the U.S. Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank (ECB) beginning their interest rate-cutting cycle by the first half of 2024. The economic recovery momentum can potentially buoy the demand prospects for NR by the fourth quarter of 2024. The improving demand prospects can make auto-tire manufacturing companies aggressive in sourcing NR ahead of the subsequent off-season of NR production. It implies that the tight supply condition can prevail even beyond Aug 2024 in view of a potential rebound in the demand, especially from the U.S. and Europe.
The tight supply condition potentially emerging by March 2024 and its subsequent exacerbation signal the possibility of NR prices undergoing a trend-break by the end of the first quarter of 2024. The uptrend can begin even earlier as speculative investors start betting on the imminent global shortage.
Will the Uptrend Sustain?
Once the prices rebound, farmers will be enthused to increase the output by adopting various short-term measures to enhance the yield of latex from their existing trees. This can markedly take the supply higher when farmers resume tapping after the ‘wintering’ off-season. The favorable prices are likely to take world supply up as farmers the world over try to extract the maximum yield from their holdings. The large extent of mature trees that have been left idle over several years in Indonesia, Thailand, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka will be re-opened for tapping once the prices become attractive.
How much additional supply can be expected in each country in response to the expected upswing in prices?
Once the world supply markedly increases following the upswing in the prices, how will it impact the supply-demand fundamentals?
Can the expected upswing in the prices sustain beyond mid-2024?
For a closer understanding of the emerging supply-demand fundamental and price dynamics for the short, medium, and long term, covering the period up to 2030, please refer to the Monthly Report available at www.whatnextrubber.com
Link: https://whatnextrubber.com/reports/
Please share your feedback in the comment box or email at contact@whatnextrubber.com
Author
Jom Jacob
Chief Analyst & Co-Founder, WhatNext Rubber Media International

Get in Touch. Get Involved.
Vivamus suscipit tortor eget felis porttitor volutpat. Nulla quis lorem ut libero malesuada feugiat. Vivamus suscipit tortor eget felis porttitor volutpat. Proin eget tortor risus.